
Ripple made it to the headline for its $1 billion acquisition of GTreasury to drive its next phase in real-time treasury and liquidity solutions. However, XRP’s price did not enjoy the boost that many traders expected. Instead of bullish momentum, XRP fell sharply, losing 5.6% in just one day.
XRP saw its market cap shrink by 5.75% to $137.21 billion. Even with intraday volumes at $7.58 billion, the mood soured fast, leaving prices scraping a 24-hour low of $2.29. This is nerve-racking!! Any which ways, join me as I decode the potential XRP price targets for the short-term.
Ripple XRP Price Analysis, Oversold Yet Not Out?
Looking at XRP’s latest price action, the technical landscape paints a challenging picture. The most critical event has been the breakdown beneath the key $2.47 support level, plunging XRP firmly into a $2.27 zone. This support loss coincided with a negative turn in the MACD histogram and a daily RSI dropping to heavily oversold values.
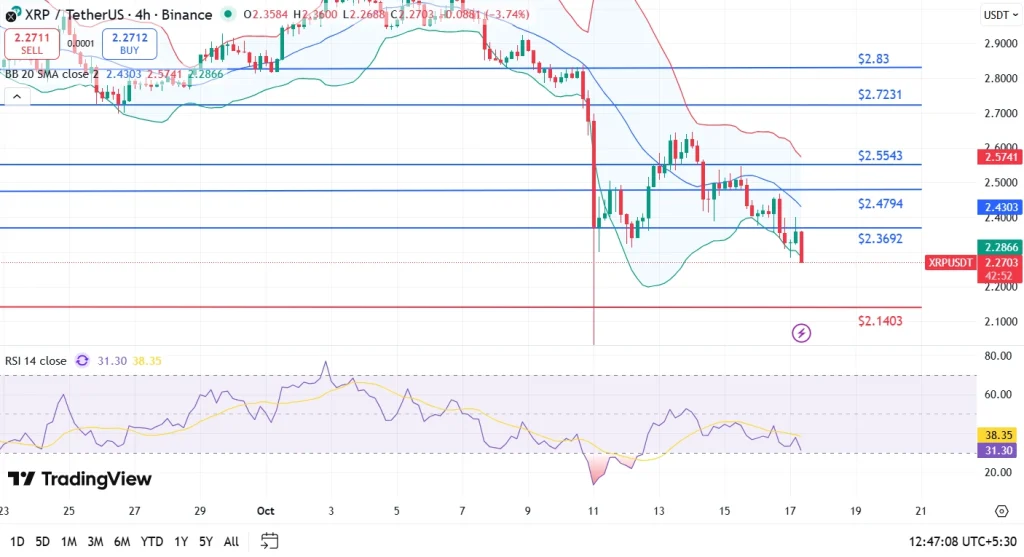
Successively, the recent chart moves also reflect repeated failed attempts to reclaim $2.47. If the price closes below the current $2.29 zone, downside targets around $2.14 come firmly into play, with the next visible support likely there. Until XRP can decisively reclaim $2.47, short-term rallies may remain capped, and risk lingers for further drops.
FAQs
Ripple’s $1B GTreasury deal boosted corporate credibility. However, market-wide risk aversion and technical breakdowns overpowered any positive news.
The XRP price today is hovering around $2.29, with an intraday change of -5.6%.
If XRP closes under $2.29, the next critical support sits at $2.14.

