Ripple’s XRP is a peer-to-peer private centralized cryptocurrency based on a distributed consensus ledger. The Ripple platform facilitates money transfers, focusing on low operation fees and lightning-like transaction speed.
Ripple is the world’s only corporate crypto solution for global payments. Some argue that Ripple cannot even be called a cryptocurrency, while others are confident that this is the most promising digital asset. This platform aims to become the next big thing in the payment systems industry and is already widely used by financial institutions worldwide.
What is the Ripple consensus protocol like? How was the idea of such a platform conceived and what exactly can it do? Let’s take a look at what Ripple (XRP) is all about!
Ripple Overview
Ripple is first and foremost a money transfer and payment ecosystem. It has a broad scope of application. Ripple is used as:
- A means of low fee currency exchange. Ripple significantly reduces transaction costs because of the low commissions it charges.
- A way to transfer funds cross-border at high speed. Money transfers through Ripple are nearly instant and take four seconds on average, which is much faster than those of other payment systems.
- It can also be used for P2P purchases, online voting, escrow, and so on.
How Does Ripple Work?
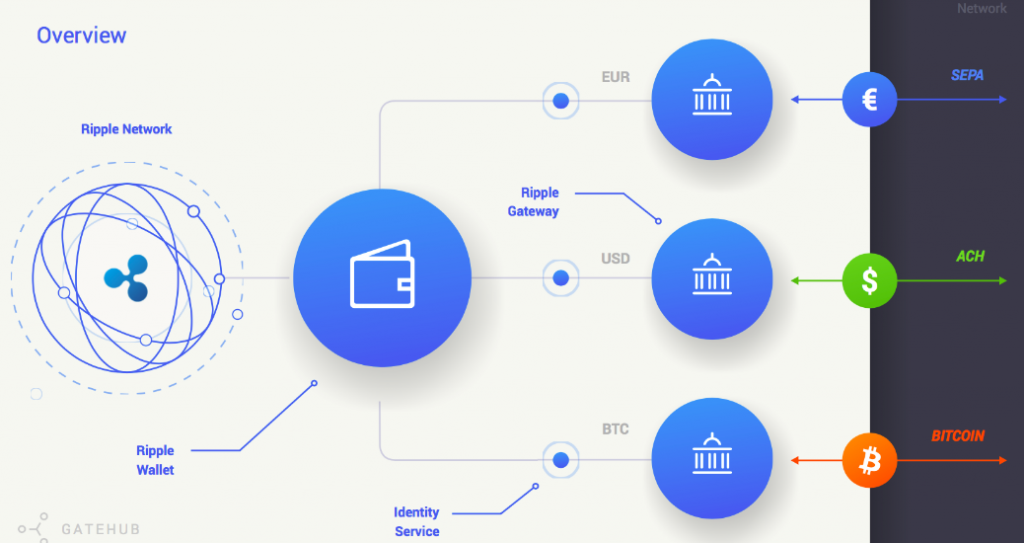
XRP is the native cryptocurrency of the XRP Ledger and the Ripple network. Its primary function is to serve as a bridge currency for cross-border transactions when there is a need to trade one currency for another. Ripple quickly attracted the attention of major institutional investors like large banks. Today, hundreds of financial companies around the world use this coin. The main advantages of XRP are the high speed and low cost of transactions.
To put it simply, Ripple works as a medium currency. Say you want to trade some JPY for USD. If you do it through the Ripple protocol, the network turns your JPY into XRP and then XRP into USD. Intuitively this arrangement seems more complicated than a simple JPY to USD exchange, but it is much faster and a lot cheaper. It takes only five to ten seconds to complete this particular transaction, compared to three to five days in the case of a traditional procedure. As for the fee, Ripple users enjoy an almost non-existent commission of 0.00001 XRP per transaction.
What Makes XRP a Unique Cryptocurrency?
Ripple (and its digital currency, XRP) differentiates itself from traditional cryptocurrencies in several key ways. Here’s a breakdown of how and why Ripple departs from the norms of other cryptocurrencies and how its underlying system operates:
- Centralization vs. Decentralization: Traditional cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum were built with the core principle of decentralization. In other words, no single entity or organization has control over the entire network. Ripple, on the other hand, is often criticized for being more centralized due to the significant role Ripple Labs plays in its development and the distribution of XRP.
- Purpose and Design: Bitcoin was introduced as an alternative to traditional currencies, allowing peer-to-peer transactions without a central authority. Ethereum was developed as a platform for decentralized apps and smart contracts. Ripple and XRP, however, were specifically designed for banks and financial institutions to facilitate real-time gross settlement system, currency exchange, and remittance.
- Consensus Mechanism: Ripple doesn’t use proof of stake (PoS) or proof of work (PoW), the two most common consensus mechanisms in the cryptocurrency world.
- Proof of Work (PoW): Used by Bitcoin, this mechanism involves solving complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks. This is energy-intensive and is commonly referred to as “mining.”
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Here, validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” or lock up as collateral.
Ripple’s Distinctive Ledger Technology and Consensus Mechanism
Ripple, known for its remittance network and real-time gross settlement system, fundamentally departs from traditional crypto approaches in its design and objectives. Its primary goal is to optimize financial transactions, particularly in the realm of international transfers, making them quicker, more transparent, and efficient.
At the core of Ripple’s system lies its innovative ledger technology. Unlike the standard blockchain structures of most cryptocurrencies, Ripple’s ledger is maintained by a network of independent servers that compare their transaction records in real-time. This real-time settlement capability is a game-changer for financial institutions and remittance services, ensuring transactions are completed in seconds.
Nodes, in the context of Ripple, play a crucial role. They use something called “node lists,” a selected list of validators that each node listens to and trusts not to defraud the system. This list of validators collaboratively decides on the validity of transactions.
An essential feature of Ripple’s design is its partnerships with banks and other financial entities. By integrating with their systems, Ripple aims to streamline cross-border payments and offer a robust remittance service. These partnerships allow XRP, Ripple’s native cryptocurrency, to act as a bridge currency in financial transactions. It’s no wonder that many major crypto exchanges list XRP given its increasing relevance in the financial sector.
Moreover, Ripple’s lack of reliance on traditional consensus mechanisms like proof of work or proof of stake sets it apart. Instead of rewarding crypto miners, Ripple’s system involves validators. These validators do not earn rewards for their efforts, eliminating financial biases. They operate based on trust, using their node lists to compare transaction records.
In essence, Ripple’s design, driven by its unique ledger technology and its focus on real-time settlement, has made it a preferred choice for many banks and remittance services worldwide. Its continued growth and integration into financial systems attest to its potential to redefine how we view and handle financial transactions.
What is RippleNet?
It is necessary to distinguish between the RippleNet system and Ripple tokens. Most banks work with the payment system, and the cryptocurrency is tied to the On-Demand Liquidity project. Therefore, the development of RippleNet does not always lead to an increase in the value of XRP.
RippleNet is a global payment system that makes it possible to carry out payments and exchange processes (transfers) in more than 40 currencies. It serves over 300 financial institutions around the world. Earlier (until the fall of 2019), RippleNet included three products: xVia, xCurrent, and xRapid.
- xCurrent is the software aimed to provide interoperation between different ledgers and payments networks using Interledger Protocol. Basically, it allows banks to communicate with each other and easily confirm payment details.
- xRapid is the source of liquidity for the network: it enables XRP to be a bridge currency and facilitates fast exchange with a stable rate.
- xVia is a payment interface that is simply used to send payments between users.
In October 2019, Ripple rebranded and split its products into two separate projects. Now the name RippleNet covers two existing products: xVia, xCurrent. The xRapid product, tied to the promotion of the XRP cryptocurrency, has been dubbed “Liquidity on Demand”.
“Instead of buying xCurrent or xVia, customers will connect to RippleNet on-premises or in the cloud, and instead of buying xRapid, they will use On-Demand Liquidity. These are not new products, but a rebranding of existing products. This is a small change that will not affect our customers in any way,” – the company representatives said.
What Is the Ripple Protocol Consensus Algorithm (RPCA)?
The Ripple network is powered by the Ripple Protocol Consensus Algorithm. It doesn’t work like the popular proof-of-work or proof-of-stake protocols. Instead, it provides a consensus validation for the ecosystem’s accounts and transactions by a number of independent nodes. For an operation to be validated, all nodes have to agree on it, and that’s the only way the operation will be executed. This protocol allows the system to prevent double-spending, primarily by taking a poll to determine the majority vote.
Ripple won’t allow you to spend the same amount of money twice or multiple times because the system determines which transaction was the first to be requested and deletes all the following ones. This consensus protocol takes mere seconds to complete the validation process, so the transaction time is minimal: it takes around four seconds on average to complete an operation.
Ripple protocol works through gateways. Gateway is an intermediary used as a link in the trust chain between two parties that want to complete a transaction. Usually, banks are those getaways. Ripple architecture is similar to that of SWIFT, a global fast payment system.
What Is Ripple’s Xpring?
Xpring (pronounced “spring”) is an ecosystem initiative by Ripple Labs that focuses on investing in, incubating, acquiring, and providing grants to projects and companies that can help expand the use cases for XRP beyond just international transactions. It aims to support the blockchain technology adoption and the development of innovative crypto solutions for various sectors.
As part of Ripple’s commitment to the growth and adoption of XRP, Xpring actively seeks out opportunities to invest in startups and initiatives that align with its vision. Through strategic investments, Xpring aims to foster the development of new technologies and applications that can leverage the unique features of XRP.
Beyond investing, Xpring also offers support through incubation and acquisition. By working closely with promising startups, Xpring provides them with access to expertise, resources, and networks necessary for their growth and success. Additionally, Xpring seeks acquisitions that can further accelerate the adoption of XRP and contribute to the overall expansion of the Ripple ecosystem.
Furthermore, Xpring provides grants to open-source projects and developers who are building tools, applications, and infrastructure that utilize XRP. These grants help foster the development of new use cases for XRP and drive innovation within the crypto space.
Ripple History
In 2004, Canadian programmer Ryan Fugger and Jed McCaleb founded Ripplepay, a payment system based on a trusted peer-to-peer financial network.

In 2012, the team was joined by the famous programmer Chris Larsen, the founder of the loan companies Prosper and E-Loan, who later became the director of Ripple Labs. He approached Fugger with the idea of creating his own cryptographic currency inside the Ripple platform, although initially, there was no talk of his own virtual currency. The development team then founded the OpenCoin corporation and launched a new cryptocurrency platform Ripple, with the same name internal currency (XRP).
In the fall of 2013, a rebranding took place, and the OpenCoin company became known as Ripple Labs. In 2014-2019, Ripple Labs Inc. focused on the banking market. The first bank to use Ripple was Fidor Bank in Munich.
Then the technology was used by the American banks Cross River Bank, CBW Bank, the Earthport payment service (works in 65 countries, including with banks). In 2017, the Ripple protocol began to be used for international payments between the US and the UK (American Express and Santander), as well as between Japan and South Korea. In 2018, the system was integrated into one of the largest eastern banks NKB in Saudi Arabia.
The SEC’s Lawsuit Against Ripple
The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) initiated a lawsuit against Ripple Labs, the entity behind the cryptocurrency token XRP, in December 2020. The crux of the lawsuit centered on allegations that Ripple conducted an unregistered securities offering, purportedly raising over $1.3 billion through the sale of XRP. The SEC posited that the XRP tokens were akin to investment contracts, and thus, should be under the purview of federal securities regulations. Ripple, in response, staunchly contested these allegations.
A pivotal turn in the case surfaced in July 2023 when a federal judge Analisa Torres ruled that although XRP offerings weren’t considered investment contracts, the initial sale of XRP had indeed contravened federal securities laws. This judgment not only has repercussions for Ripple but also sets a precedent concerning the SEC’s perspective on digital assets. It implies that Ripple need not categorize XRP as a security in the future, but it casts a shadow on the legality of XRP’s inaugural sale and the probable ramifications for breaching securities statutes.
Fast forward to October 19, 2023, the SEC retracted its charges against Ripple’s CEO, Brad Garlinghouse, and Chairman, Chris Larsen. This absolution essentially exonerates Ripple’s leadership from the longstanding securities violation claims that had been navigating the intricacies of the federal legal system. Moreover, the charges annulled were linked to institutional sales set for trial the following April.
Is the SEC vs. Ripple Case Over?
Not quite. While some charges have been dropped, Ripple remains steadfast in its pursuit of greater regulatory lucidity within the U.S. framework.
The SEC, in its latest filing, emphasized its intent to persist with claims against Ripple. Both parties, it said, “plan to convene to discuss the forthcoming phases of the case, specifically addressing appropriate remedies concerning Ripple’s Section 5 infringements related to its Institutional Sales of XRP.”
The legal tussle between the SEC and Ripple has garnered considerable attention from the crypto community and is perceived as a watershed moment for the sector. The final verdict is poised to influence future regulatory guidelines and protocols for digital currencies.
Can Ripple (XRP) Be Staked?
Since XRP is neither a proof-of-work nor proof-of-stake cryptocurrency, it cannot be mined or staked. However, that does not mean you can’t earn interest on your Ripple crypto coins. There are some platforms that allow you to make money off of this cryptocurrency. Some of these services include Nexo, Crypto.com, and Binance Earn.
Ripple Advantages & Disadvantages
The XRP currency has a legal entity, representative office, and headquarters in the United States. This makes it attractive to investors from a capital investment reliability standpoint. At the same time, this can also be considered a drawback as it makes the network more centralized than other crypto projects.
Ripple cannot be mined. The developers abandoned the idea of mining coins and released 100 billion XRP tokens all at once. Each coin is divided into a million parts, called drops. At the same time, coins are no longer issued. This can also be considered both a pro and a con of this cryptocurrency depending on what your goals and preferences are.
One of the biggest advantages of the XRP consensus ledger is its high transaction speed. For example, while Bitcoin transactions can take around 600 seconds, XRP ones only take 4.
Pros and Cons of Ripple’s XRP Cryptocurrency
Ripple’s XRP, the digital heartbeat of the Ripple network, stands tall in the sprawling landscape of cryptocurrencies. Its distinct framework and applications present a mix of advantages and challenges worth delving into.
Pros
- Speedy, Cost-Efficient Transactions: XRP distinguishes itself with its consensus protocol, sidestepping the time-consuming and energy-intensive mining processes seen in networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum. The absence of miners results in swift transaction confirmations and negligible fees.
- Bridge Currency Functionality: With Ripple’s alliances with global banks and financial entities, XRP streamlines cross-border money movements. This synergy with Ripple’s payment ecosystem translates to almost instantaneous, low-fee, and secure international transactions, outpacing conventional, pricier methods.
- Real-time Liquidity Access: A standout feature of Ripple’s tech toolkit is the effortless conversion between any currency and XRP. For financial institutions, this obviates the necessity of maintaining vast foreign currency reserves, trimming expenses and enhancing operational agility.
Cons
- Connection with Ripple Labs: Ripple Labs, the private entity that owns a sizable XRP tokens, is a double-edged sword. Detractors believe such concentrated ownership contradicts the decentralized ethos of cryptocurrencies, prompting introspection about XRP’s autonomy as a digital currency.
- Regulatory Clouds: Ripple Labs’ ongoing legal skirmish with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) casts a shadow over XRP’s future. Accusations that XRP’s initial sale breached federal securities regulations could impact its legal standing and market reception.
- Validator Centralization Concerns: Ripple’s decentralized validator network isn’t without criticism. Concerns simmer about Ripple’s outsized sway over validator selection and the overall XRP ledger function, potentially threatening the network’s decentralized character and security.
Ripple vs Bitcoin
Ripple is one of the biggest cryptocurrencies in the world – it has been ranked within the top 10 by market capitalization for a very long time. As a result, it naturally gets compared to Bitcoin a lot.
These two cryptocurrencies, however, couldn’t have been more different. For one, let’s take a look at their purposes: BTC is meant to be a method of exchange, while Ripple is a global payments network capable of conducting cross-border payments in a cheap and efficient way.
Still, both BTC and XRP can be used as digital assets, traded and exchanged for profit. Bitcoin has a higher market cap and profit-making potential, while XRP is focused on adoption and cooperation with existing financial institutions, which may make it more reliable in the long run. Additionally, XRP transactions are a lot faster and cheaper than the ones on the Bitcoin network – so they are a lot more efficient and thus attractive to users.
How To Buy Ripple
You can buy XRP on most cryptocurrency exchanges. If you’re looking for a platform that is both easy to use and has great rates with low fees, look no further than our marketplace, Changelly!
You can use our website or mobile app to either get Ripple with one of the 200+ cryptocurrencies we have previously listed on our service or buy it with one of the over 40 fiat currencies supported by our fiat gateway partners. Here’s a step-by-step guide to buying XRP on Changelly.
- Go to changelly.com/buy.
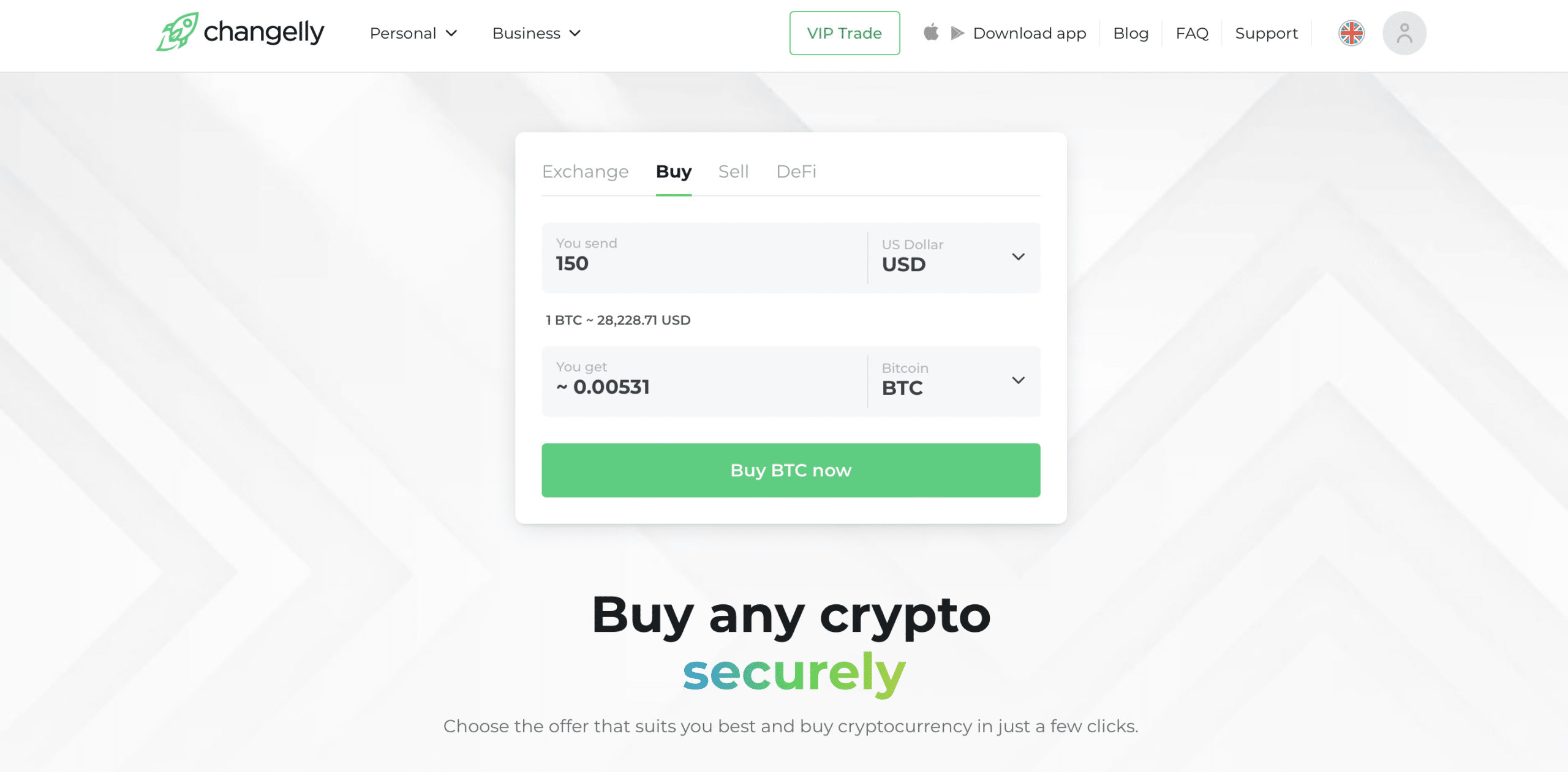
- Select XRP from the dropdown menu and the fiat currency you want to use to buy it.
- Enter the amount you are going to spend and select your payment method.
- You’ll be presented with a selection of fiat providers. Pick the one you like the most.
- Enter the address of the wallet that you want your XRP tokens to be sent to and the Destination Tag.
- Agree to the Terms of Use and click on the “Buy” button below to proceed. You will be redirected to our partner’s website – follow their instructions to get your XRP.
FAQ
Is Ripple and XRP the same?
Ripple is the name of a company. It is a global payment settlement network. XRP is the native digital currency of that platform.
What is Ripple famous for?
Ripple is renowned for its digital payment network and protocol, providing a platform for seamless financial transactions.
How is Ripple making money?
Ripple generates revenue through the sale of its cryptocurrency, XRP, coupled with payment fees. Additionally, they garner profits from investments and collect interest fees on loans.
What is Ripple (XRP) used for?
XRP acts as an intermediary between two currencies or networks. Simply put, it can give other currencies a more efficient way to conduct transactions.
Is Ripple (XRP) a good investment?
XRP can be a great addition to your portfolio. It has a high market cap and good future prospects. However, you should do your own research before deciding whether you should invest in it or not.
Is XRP better than Bitcoin?
It’s hard to compare these two as they serve different purposes. When considering XRP as an independent digital asset, however, and not a part of a global payment network, it can lose out to BTC as it is less popular and widespread.
Who are the founders of Ripple?
Ripple Labs founders are Chris Larsen and Jed McCaleb.
Disclaimer: Please note that the contents of this article are not financial or investing advice. The information provided in this article is the author’s opinion only and should not be considered as offering trading or investing recommendations. We do not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this information. The cryptocurrency market suffers from high volatility and occasional arbitrary movements. Any investor, trader, or regular crypto users should research multiple viewpoints and be familiar with all local regulations before committing to an investment.