When it comes to money management, many people struggle to understand the difference between saving and investing. Are you confused about where to put your hard-earned money? It’s important to grasp the distinction between saving and investing in order to make smart financial decisions.
In today’s economic climate, individuals are constantly bombarded with advice on how to manage their money. However, the concept of saving versus investing is often overlooked or misunderstood. Both saving and investing have their own benefits and risks, and one should know how they differ in order to achieve one’s financial goals.
In this article, we will explore the key differences between saving and investing and provide guidance on how to make the most of both strategies.
What Is Saving?
At its core, saving involves putting money aside for future use, typically in a secure and accessible place such as a savings account, money market fund, certificate of deposit, or a similar financial product. This financial strategy is characterized by its safety and accessibility, offering a haven for your funds with the trade-off of relatively lower returns. The essence of saving is to provide a financial buffer and immediate liquidity for unforeseen needs or short-term goals.
Example
Imagine you’re planning to buy a new car next year, or perhaps you’re building an emergency fund to cover six months’ worth of living expenses. In these scenarios, saving is your go-to strategy. By allocating a portion of your income into a savings account, you’re not only preparing for future expenses but also ensuring that your money remains readily accessible should you need it unexpectedly.
What Is Investing?
Investing, on the other hand, is the process of using your money to purchase assets with the expectation of generating a return over time. Unlike saving, investing comes with the potential for higher returns, albeit at a higher risk. The goal of investing is to put your money to work, growing it over the long term through the power of compound interest and market gains.
Example
Consider the decision to purchase shares in a company, buy a piece of real estate, or invest in bonds. These are all forms of investing where your money is expected to earn a return over time. For instance, buying stocks in well-performing companies can offer significant growth potential, turning your initial investment into a much larger sum in the future. Similarly, investments in real estate could generate rental income and appreciate in value, providing a solid foundation for your financial future.
Read also: Mutual funds vs. ETFs.
In both saving and investing, the underlying principle is to ensure your financial stability and growth. However, the path you choose depends on your financial situation, goals, and risk tolerance. As we examine the differences between these two strategies, keep in mind that both are integral to a well-rounded financial plan.
4 Key Differences Between Saving and Investing`
Understanding the nuances between saving and investing is pivotal for anyone looking to secure their financial future. While both strategies serve the purpose of growing your wealth, they cater to different needs and objectives. Delving into the four key differences between saving and investing will illuminate how each approach can serve your financial journey.
1. Risk and Return
The dichotomy of risk and return is perhaps the most significant distinction between saving and investing. Investing often involves placing your money into financial instruments that, while carrying the potential for higher returns, also have an increased level of risk. The stock market, real estate, and mutual funds are prime examples where returns are not guaranteed, and the value of your investments can fluctuate widely based on market conditions.
On the flip side, saving is characterized by a much lower risk profile. When you put your money into savings, such as in a savings account, the risk of losing the principal is minimal. However, this safety comes at the cost of lower returns. The interest rates on savings accounts are typically modest, especially compared to the potential gains from investments. This fundamental trade-off between risk and return is crucial in determining whether your money should go into savings or be channeled towards investment opportunities.
2. Liquidity
Liquidity refers to how quickly and easily an asset can be converted into cash without significantly affecting its value. Savings accounts excel in this area, providing unparalleled access to funds. This liquidity makes savings a perfect fit for emergency funds or short-term financial needs, where immediate access to your money is paramount.
Investments, however, tend to be less liquid. Besides taking more time, selling stocks or withdrawing money from a retirement account can have financial implications, such as market losses or penalties. The reduced liquidity of investments is a trade-off for the potential of higher returns, making them more suited to long-term financial planning where the money can remain invested for extended periods.
3. Short and Long-Term Goal Setting
Your financial goals play a significant role in deciding whether to save or invest. Savings are ideal for short-term goals due to their stability and liquidity. Whether it’s a savings goal for a vacation, a down payment on a house, or an emergency fund, putting your money into savings ensures that it will be there when you need it, without the risk of value fluctuations.
Investing, conversely, is tailored towards long-term investment objectives. If your future goals include retirement, funding a child’s education, or any other objective that’s more than five years away, investing offers the opportunity to grow your money over time, outpacing inflation and increasing your purchasing power. Recognizing the timeframe of your financial ambitions can guide you in choosing the right approach to meet your needs.
4. Inflation Hedging
Inflation represents the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services rises, subsequently eroding purchasing power. One of the pitfalls of keeping your money in savings over time is its vulnerability to inflation. The modest interest rates offered by savings accounts often fail to keep pace with inflation, meaning your savings could lose value in real terms over the years.
Investing, however, can serve as an effective hedge against inflation. By carefully selecting a mix of investments, such as stocks or real estate, you can achieve returns that not only match but potentially exceed the rate of inflation, preserving or even increasing your wealth’s purchasing power. This makes long-term investment strategies an essential component of any plan to secure your financial future and ensure that your money retains its value over time.
Each approach has its benefits and drawbacks that influence when and how you should allocate your funds. Let’s explore the pros and cons of saving and investing—tune in for practical advice on when to utilize each strategy to meet your financial objectives.
Pros and Cons of Saving
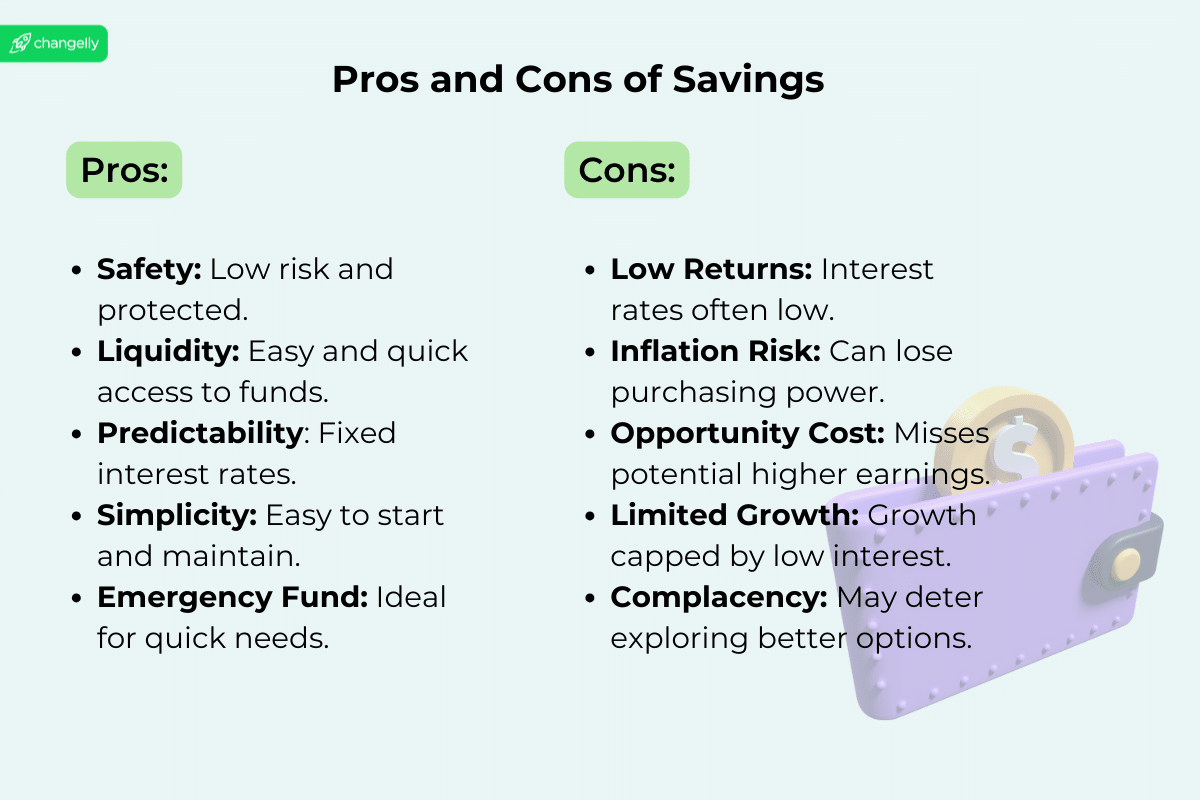
Pros:
- Safety: Savings accounts are typically insured by government agencies, such as the FDIC in the United States, up to certain limits, which offers a high degree of safety for your money.
- Liquidity: Savings accounts are ideal for emergency funds or short-term financial needs, ensuring you can get to your money when you need it without delay.
- Ease of Access: Savings accounts are straightforward to open and manage, making them accessible to everyone regardless of their financial knowledge.
Cons:
- Low Interest Rates: The interest rates on savings accounts are often low, especially in comparison to potential returns from investments. This can make it challenging for your savings to grow over time.
- Impact of Inflation: Savings can lose purchasing power over time due to inflation. The interest earned on savings accounts frequently fails to keep pace with the rate of inflation, diminishing the real value of your money.
One important note: While savings accounts offer a secure place for your funds, the real value of these savings could erode over time due to the relatively low interest rates and inflation. Incorporating statistics from reputable financial institutions can further validate these points, emphasizing the importance of strategic financial planning.
Pros and Cons of Investing
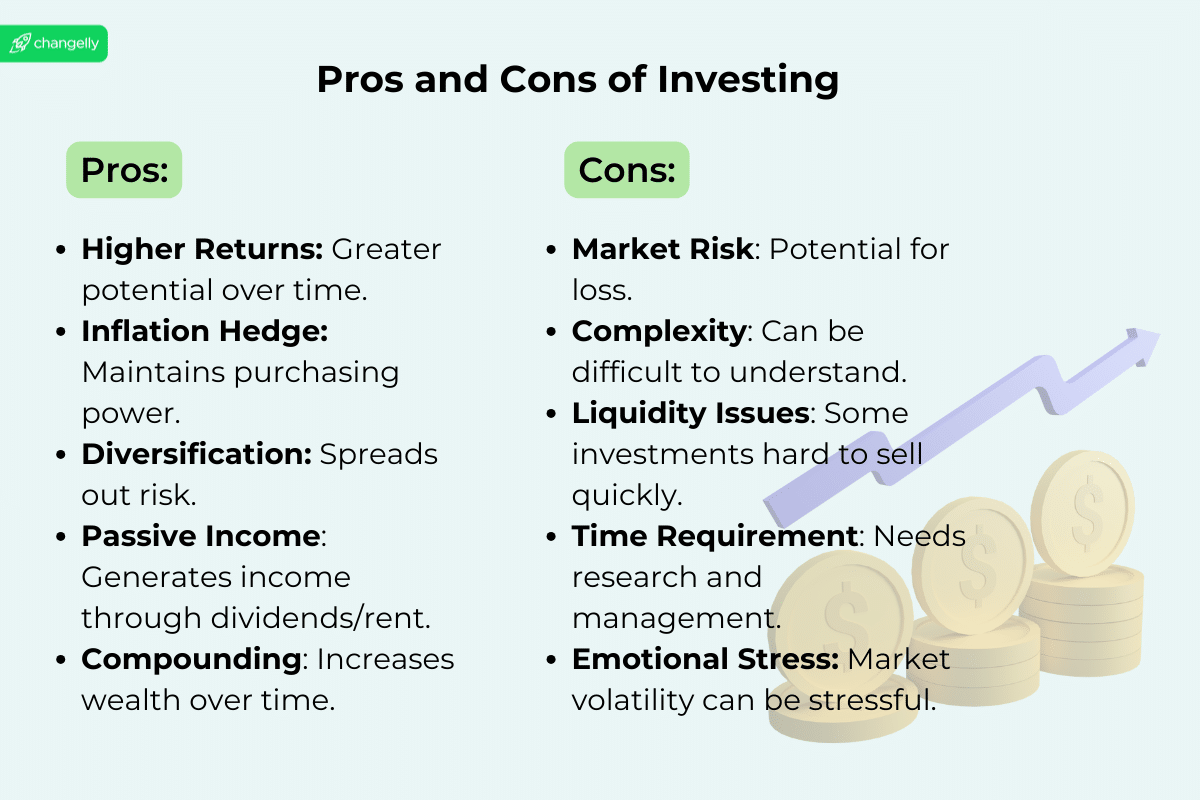
Pros:
- Higher Returns: Investing can provide higher potential returns compared to traditional savings accounts. Over the long term, well-chosen investments can significantly outpace inflation and contribute to wealth accumulation.
- Compounding Benefits: Investments can benefit from compounding, where returns on your investments generate their own returns over time. This can exponentially grow your wealth.
- Inflation Hedging: Investments, particularly in stocks and real estate, have historically outperformed inflation, helping to preserve the purchasing power of your money.
Cons:
- Risks: Investing involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. The value of investments can fluctuate based on market conditions, economic factors, and company performance.
- Need for Research: Making informed investment decisions requires research and a solid understanding of the market, which can be daunting for new investors.
- Potential for Loss: Unlike savings accounts, investments can decrease in value, and there’s no guarantee of returns, which means you could lose money.
Historical data underscore the advantages of investing, such as the long-term growth seen in the stock market and real estate investments. Many examples highlight the potential for significant returns while also acknowledging the inherent risks and the importance of research and risk management.
Read also: Best AI Stock to Buy.
When to Save
In the landscape of personal finance, the habit of saving embodies a foundational principle for securing immediate financial stability and preparing for short-term objectives. Engaging in the practice of setting aside cash savings plays a crucial role, especially when gearing up for near-future expenditures or establishing a robust emergency savings fund.
Situations that underscore the importance of saving include:
- Building an Emergency Fund: As a rule of thumb, it’s wise to accumulate an emergency fund covering 3–6 months of living expenses. This financial cushion safeguards against unexpected events—be it job loss, medical emergencies, or urgent home repairs—ensuring that unforeseen challenges do not derail your financial stability.
- Saving for Near-Term Purchases: Whether it’s for acquiring a vehicle or indulging in a well-deserved vacation, saving targets specific, short-term goals. This approach offers peace of mind that comes with knowing your aspirations are within reach, without compromising your financial well-being.
- Prioritizing Stability and Liquidity: When the certainty of accessing your funds without delay outweighs the allure of a higher rate of return, saving becomes the strategy of choice. This is particularly relevant for individuals who foresee a need to tap into their funds on short notice, underscoring the value of liquidity and the security provided by immediate cash reserves.
When to Invest
Venturing into the realm of investing marks the commencement of an investment journey aimed at achieving longer-term goals and amplifying wealth over extended periods. This strategy is distinguished by its focus on harnessing the power of various types of investments to secure a future that encompasses everything from retirement savings to funding a college education.
Consider investing when:
- Planning for Retirement or Long-Term Objectives: For goals that stretch far into the horizon—such as securing a comfortable retirement or providing for a child’s college education—investing emerges as a strategic choice. It’s the pursuit of a higher potential rate of return over the long term that makes investing attractive despite the inherent risk of loss associated with market fluctuations.
- You Possess a Solid Emergency Fund: Having established a stable emergency fund, you’re in a position to engage in investments with your surplus funds. This layer of financial security enables you to lock away capital in investments for prolonged durations, comfortably riding out the volatility of the market without jeopardizing your immediate financial needs.
- Eager to Build Wealth Over Time: Embarking on an investment journey with an eye toward accumulating wealth necessitates a readiness to confront and manage the risks involved. Understanding the types of investments—from stocks and bonds to real estate—and their respective risk profiles is a must. With a commitment to regular investment and a long-term perspective, the potential for compounding gains becomes a powerful tool in realizing your financial ambitions.
Read also: Is Bitcoin a Good Investment?
When Should You Move from Saving to Investment?
The transition from saving to investing marks a pivotal moment in your financial journey and indicates readiness to embrace greater potential rewards alongside increased risks. Understanding when to make this shift involves assessing several key factors, including your financial stability, risk tolerance, and overarching financial goals.
Transition Advice
- Financial Stability: Before venturing into investing, ensure you have a solid financial foundation. This includes having enough cash savings to cover living expenses for at least 3–6 months, minimizing high-interest debt, and maintaining a steady income. This level of stability provides a safety net that allows you to invest with confidence.
- Risk Tolerance: Assess your comfort with risk. The risk of loss is inherent in investing, and you must understand your capacity to endure market fluctuations without jeopardizing your financial well-being. A higher risk tolerance may lead you to invest more aggressively, while a lower tolerance suggests a more conservative approach.
- Financial Goals: Align your investment strategy with your long-term financial goals. If you’re saving for a goal that’s 5 or more years away, such as retirement or a child’s education, investing could offer the growth potential necessary to achieve these objectives.
Conclusion
Navigating the realms of saving and investing is fundamental to achieving financial security and realizing your long-term aspirations. While saving offers a safe harbor for short-term needs and emergency funds, investing unlocks the potential for substantial growth, essential for meeting more significant future goals. Recognizing when to transition from saving to investing is a critical step that hinges on your financial stability, risk tolerance, and objectives.
As we’ve explored the differences between saving and investing, the importance of choosing the right strategy for your financial situation becomes clear. The journey from saving to investing is a personal one, influenced by individual circumstances and goals.
Disclaimer: Please note that the contents of this article are not financial or investing advice. The information provided in this article is the author’s opinion only and should not be considered as offering trading or investing recommendations. We do not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this information. The cryptocurrency market suffers from high volatility and occasional arbitrary movements. Any investor, trader, or regular crypto users should research multiple viewpoints and be familiar with all local regulations before committing to an investment.

