The importance of decentralization in file sharing
Decentralized file sharing revolutionizes data access by eliminating dependency on centralized servers and using P2P technology to distribute files across a network of nodes.
Distributing and accessing data without relying on a centralized server is possible with decentralized file sharing. Instead, files are kept on a network of linked nodes, often through the use of peer-to-peer (P2P) technology.
To enable file sharing, each network user can provide bandwidth and storage space. BitTorrent and InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) are two well-known examples of decentralized file sharing protocols.
The decentralization of file sharing has completely changed the way users access and store digital content. Unlike conventional centralized file sharing systems, where files are stored on a single server, decentralized file sharing uses a P2P mechanism. Distributing files across a network of linked nodes promotes a more robust and secure system.
Key components of decentralized file sharing
Decentralized file sharing relies on a number of essential elements to enable distributed and secure data exchange.
First, P2P networks, which allow direct user contact in the absence of a centralized server, are the backbone of a decentralized file sharing system. Doing this promotes a robust system where participants share files directly.
Blockchain technology is essential for maintaining the integrity and trust in decentralized file sharing networks. It improves the overall security of transactions and file transfers by enabling transparent and impenetrable recording. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with predefined rules that automate tasks such as access control and file verification.
Furthermore, files are distributed across a network of nodes using decentralized storage systems, which often use protocols such as BitTorrent or IPFS. This approach eliminates the need for a central server and improves data availability and reliability due to its redundant nature.
Cryptographic methods also protect data integrity and privacy. User trust in decentralized file sharing systems is increased by end-to-end encryption, which ensures that only authorized parties can view the content. Together, these elements essentially provide a secure and distributed environment for easy file sharing over the decentralized Internet.
How does decentralized file sharing work?
Decentralized file sharing works on P2P networks by using a distributed architecture instead of relying on a central server.
Peer discovery
Participants in the network (peers) need a way to discover each other, which is accomplished by using distributed hash tables (DHTs) or decentralized protocols. Peers build a network without central authority by keeping track of other peers they are connected to.
DHTs are decentralized systems that enable distributed storage and retrieval of key-value pairs across a network, while decentralized protocols enforce communication rules that enable peer-to-peer interactions without reliance on a central authority or server.
File distribution
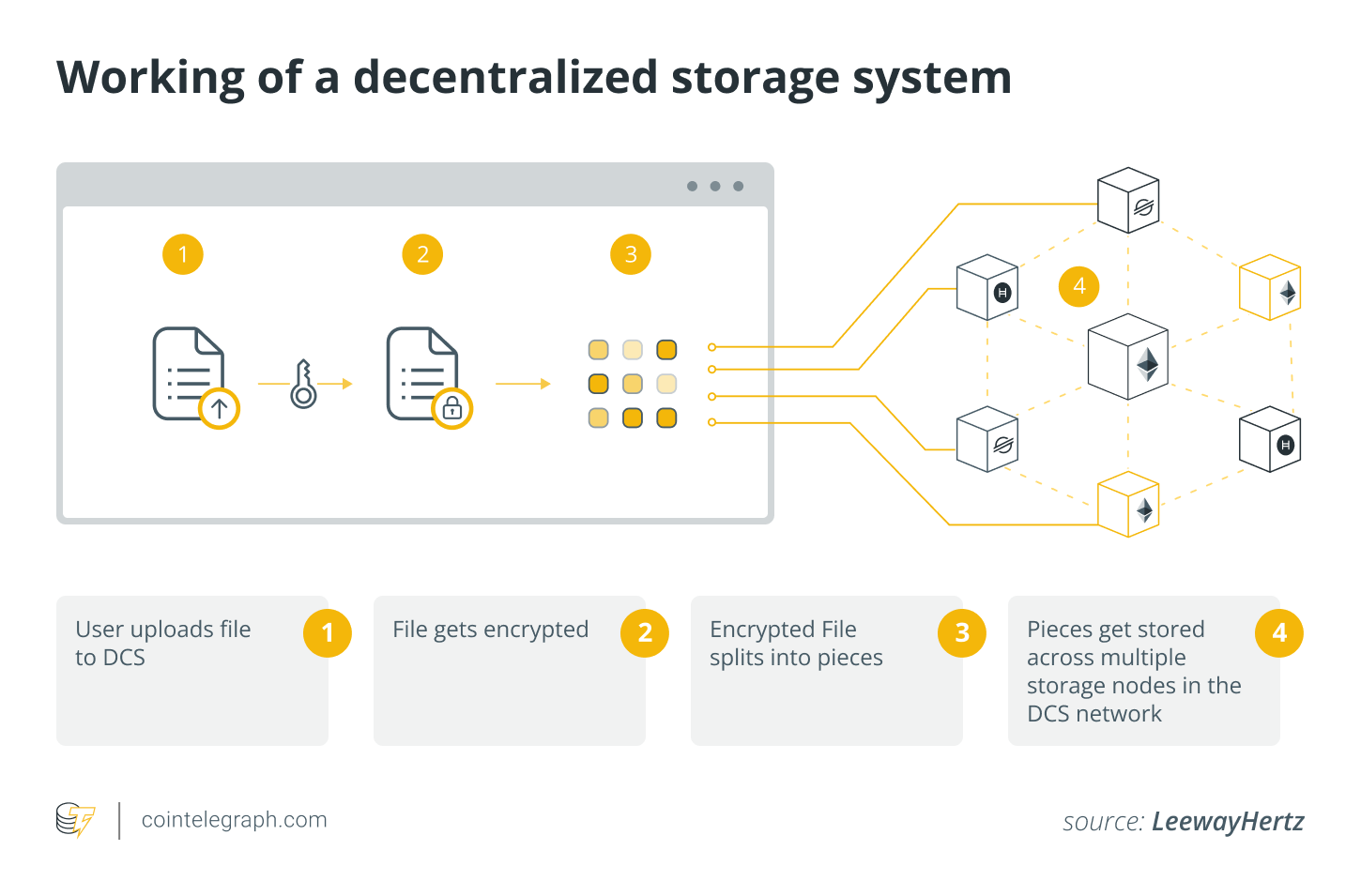
A file is split into smaller parts, with each part distributed among different network members. This approach improves the availability of files because they are not stored in one location, ensuring better accessibility and reliability.
Scattered storage
By distributing file portions across different nodes, decentralized storage systems reduce dependence on a single server. For example, IPFS uses a content-centric approach, where files are recognized by their content rather than their physical location.
Interaction with peers
Colleagues request file sections directly and share them directly with each other. Thanks to this direct connection, a central server is no longer required to coordinate file transfers. Each peer participates in the file distribution process by acting as both a client and a server.
Blockchain and smart contracts
Blockchain technology has been incorporated into several decentralized file sharing systems to increase security and transparency. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with pre-established rules that can automate tasks such as access restriction and file verification and reward participants with tokens.
Often, decentralized file sharing systems use cryptographic techniques such as end-to-end encryption to provide privacy and security for the shared files. This ensures that the content can only be accessed and deciphered by authorized users.
Benefits of decentralized file sharing
The benefits of decentralized file sharing include improved resilience, improved privacy, scalability, and censorship resistance.
Removing a single point of failure improves reliability and resilience. In a peer-to-peer network, where files are spread across several nodes and peers, the system continues to function even if some nodes fail.
Additionally, decentralized file sharing inherently provides enhanced security and privacy. By ensuring that only authorized users can access and decrypt shared content, cryptographic solutions such as end-to-end encryption help reduce the threat of unauthorized spying or data breaches.
Better scalability can also be achieved as the network grows. In decentralized networks, more users increase the capacity of the network, allowing it to accommodate more demand and traffic without requiring changes to the centralized infrastructure.
Furthermore, decentralized file sharing encourages resistance to censorship. It is more difficult for any organization to censor or restrict access to certain files or information because there is no single entity in charge of the network.
Additionally, decentralized file sharing often includes incentive mechanisms through token economies or other reward systems to encourage users to contribute resources such as bandwidth and storage, creating a cooperative and self-sustaining environment.
Challenges and limitations of decentralized file sharing
Challenges associated with decentralized file sharing include scalability issues, consistency issues, complexity of user adoption, security risks and regulatory uncertainties.
First, scalability issues become more pressing as the network grows. A poor user experience can result from increased engagement if it results in slower file retrieval times and increased bandwidth requirements.
Furthermore, in decentralized systems, consistency and coordination issues can surface. In the absence of a central authority, it can be difficult to maintain consistency in file versions across the network, leading to conflicts and inconsistent data.
Complicated interfaces and user acceptance are another problem. Compared to centralized options, decentralized file sharing platforms often have a higher learning curve, which can deter consumers who are unfamiliar with P2P networks or blockchain technology.
Furthermore, security concerns still exist, especially in the early stages of decentralized file sharing implementation. As these systems become more widely used, they become the target of various types of attacks, necessitating the continued development of strong security measures.
Regulatory uncertainty is another problem. The adoption and long-term viability of decentralized file sharing platforms may be affected by the changing legal environment surrounding cryptocurrency and decentralized technology.
The future landscape of decentralized file sharing
The future of decentralized file sharing includes blockchain technology, P2P networks and tokenization for secure, efficient and collaborative data sharing, challenging traditional models.
Decentralized file sharing is expected to lead to a more inclusive, secure and productive environment. Distributed ledger and blockchain technology will be essential for ensuring tamper-proof and transparent transactions and facilitating file sharing between users without relying on centralized intermediaries.
Decentralized protocols powering peer-to-peer networks will enable direct data transfer between users, reducing latency and dependence on centralized servers. Strong encryption techniques will eliminate privacy concerns and give consumers more control over their data.
Furthermore, tokenization could encourage resource sharing among users, resulting in the development of a collaborative ecosystem. Innovative file sharing services are likely to spread as decentralization gains momentum, upending established paradigms and fostering a more robust and democratic digital environment.

