The PWN DAO Foundation, linked to the peer-to-peer lending protocol PWN, has released a comprehensive report analyzing user-incurred onchain fees within major blockchain networks and decentralized applications (dapps) over the past year. The 2023 analysis examines Ethereum, BNB Chain, Bitcoin and layer two (L2) solutions, along with commonly used dapps such as Aave and Uniswap. The report sheds light on key trends in fee generation and discusses the changing patterns of blockchain usage and revenue.
The L1 and L2 fee generation metrics for 2023 revealed
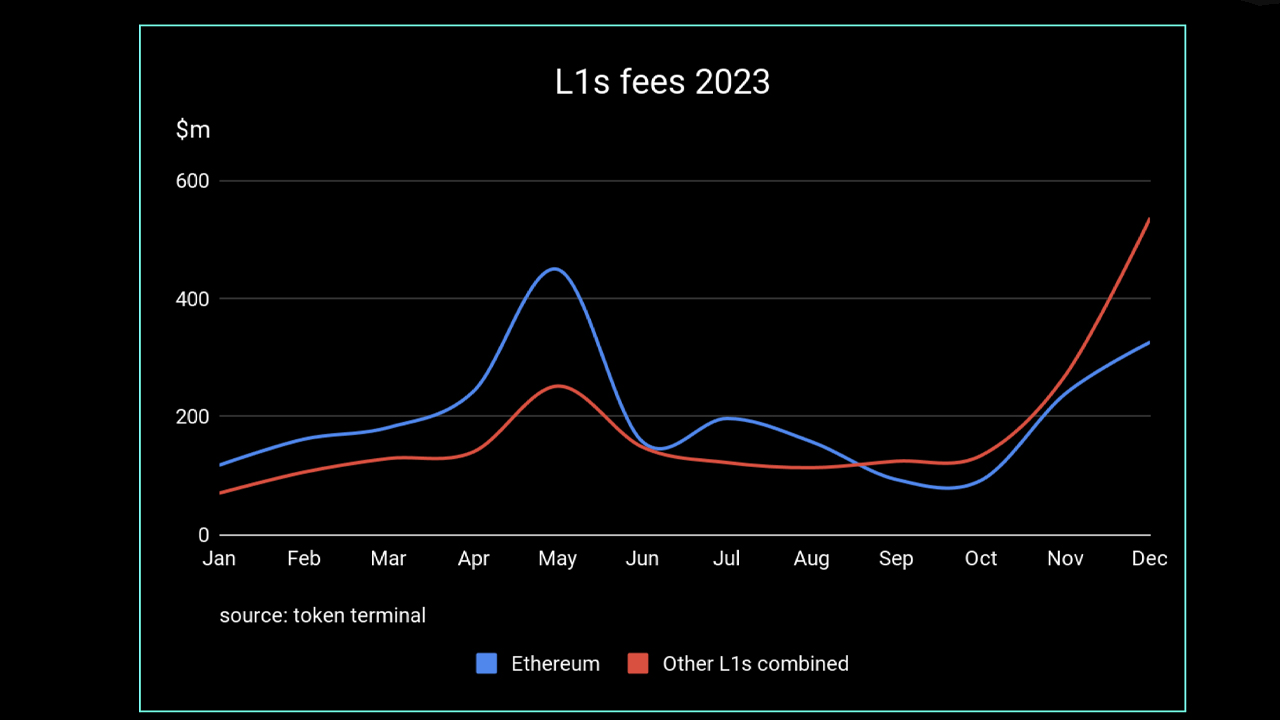
The report published by PWN illustrates a diverse landscape of onchain fees, highlighting an overall 33% reduction in fees for the selected projects compared to the previous year. This trend was especially pronounced on the non-fungible token (NFT) marketplaces, where fee generation fell by 87%. In contrast, L2 solutions showed significant growth of approximately 411%, indicating a shift in user preferences and platform usage.
Screenshot from PWN’s research called the ‘Crypto Native Economy Report’.
The research shows that despite a slight decline, layer one (L1) blockchains continued to dominate the fee market, accounting for 59% of all fees, up from 48% in 2022. Ethereum, which maintained its position as the market leader, showed a notable see growth. 44% decrease in rates, partly due to the migration of activities to L2 networks.
“The rising fees generated by [L2s] indicate widespread adoption and a significant impact on user experience,” the study authors said.
The report also highlights significant changes in individual blockchain platforms. Bitcoin, Tron, and Polkadot saw the most substantial growth in fee generation, with Bitcoin fees increasing by 461%. The rise in Bitcoin network fees was attributed to the popularity of Ordinal inscriptions, a new embedding application within the Bitcoin network, which marks a notable shift in usage dynamics. As of January 29, 2024, the number of Ordinal inscriptions on the Bitcoin blockchain has impressively crossed the 58 million mark.
Decentralized exchanges (dexs) witnessed a 51% decline in fee generation, with Uniswap emerging as a dominant player, securing 64% of dex-generated fees. The report suggests that despite the drop in fees, trading volume on dex platforms remained relatively stable, indicating an evolving relationship between trading activity and fee structures in the decentralized finance (defi) sector.
The report concludes with a discussion of liquid staking derivatives (LSDs), which showed a significant 93% increase in fee generation, highlighting the growing interest in staking solutions within the crypto-native economy. The report notes that Lido Finance, the LSD leader, has collected a significant portion of these fees, reflecting the platform’s strong position in the market.
As the landscape evolves, with user preferences moving towards more efficient and innovative platforms, it is clear that the blockchain ecosystem is continually undergoing a transformative phase. This evolution paves the way for emerging technologies and strategies, which will potentially redefine the future of blockchain utility and economic models in the crypto space.
What do you think of PWN’s report on L1s and L2s, dapps and fee generation? Let us know what you think about this topic in the comments below.

